The MEBA approach is designed to compare the short-course time-course profiles with regard to different experimental conditions. It is based on the timecourse method described by YC Tai. et al.
The result is a list of variables that are ranked by their difference in temporal profiles across different biological conditions. The Hotelling-T2 is used to rank the variables with different temporal profiles between two biological conditions under study; And the MB-statistics is used for more than two biological conditions. Higher statistical value indicates the time-course profiles are more different across the biological conditions under study. An example output from the top ranked feature is given below
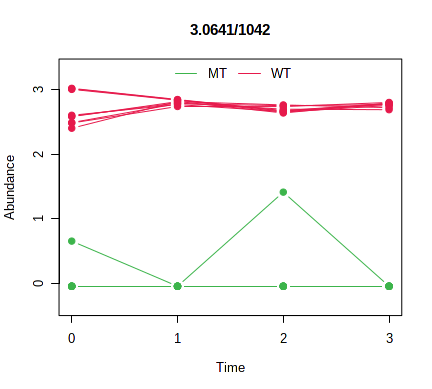
Please note, MEBA allows prioritize the features based on their temporal profiles. No associated p-values are computed in the implementation.